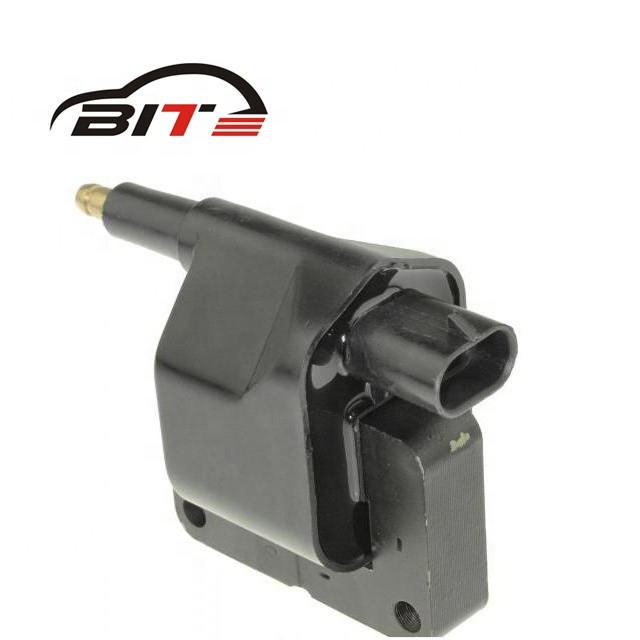
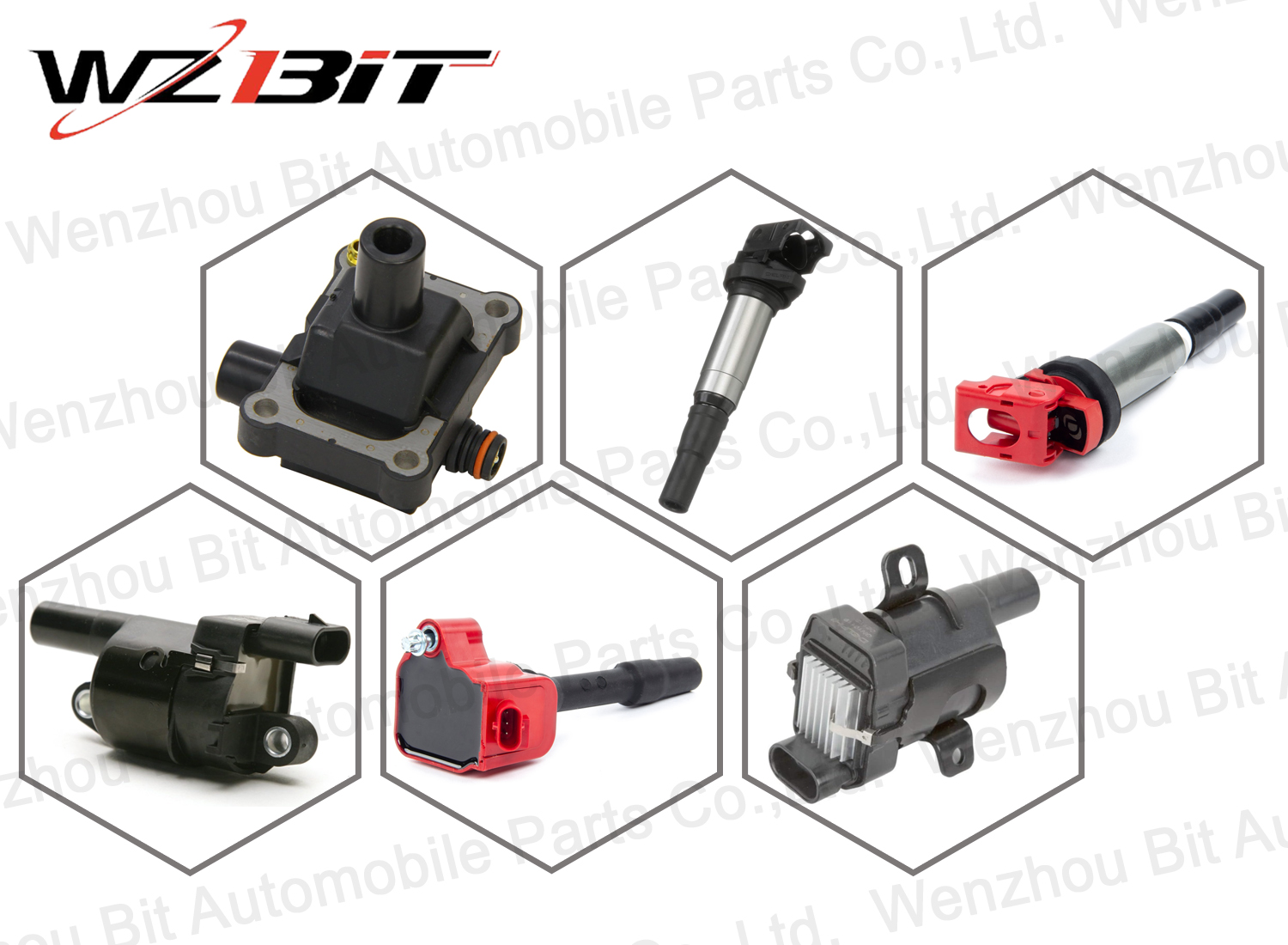
Ignition Coil
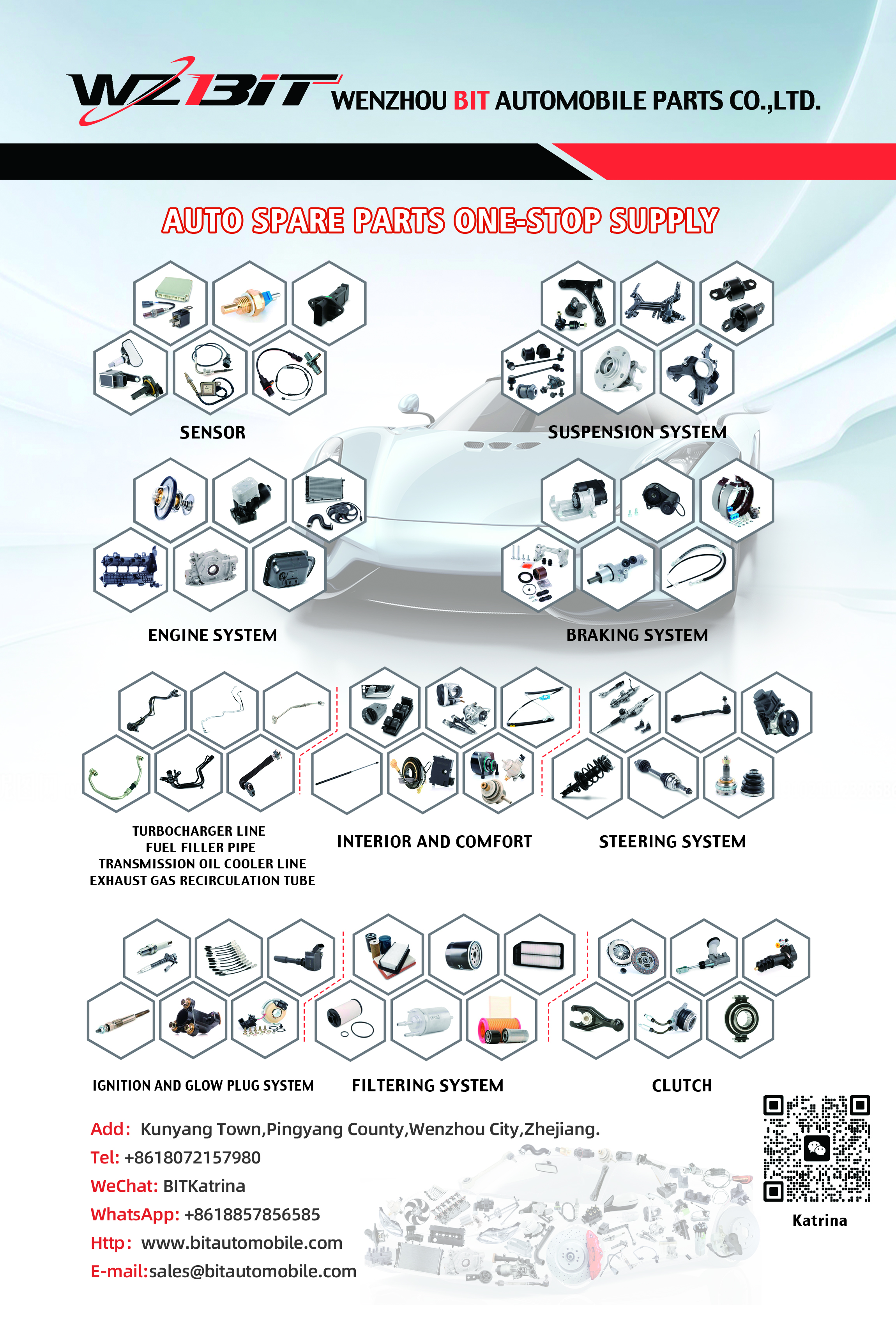
An ignition coil is a crucial component in the ignition system of internal combustion engines. Its primary function is to transform the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs. This spark is essential for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine's cylinders.

OE Nember
FTM-076
90048-52093
90048-52077
9004852110
525277
52525577
F-614
90048-52095
90048-52086
9004852076
4751253
05 234 210
F-076
00K04797293AB
90048-52085
9004852081
4797293
05 234 610
C506
9004852084000
90048-52072
9004852090
5234610
04 797 293
UF97
9004852096000
90048-52084
9004852056
5234210
05 252 577
CP-32
0048-52095-000
90048-52070
9004852066
5252577
9004852057
C932
90048-52093-000
90048-52079
9004852060
19017110
9004852102
XIC8135
90048-52091-000
90048-52078
9004852059
56027965
90048-52099
K04797293
90048-52072-000
90048-52079
9004852096
53008068
90048-52098
Compatible Applications
1991-1992 CHRYSLER DYNASTY 2.5L L4
1991-1994 CHRYSLER LEBARON 2.5L L4
1991-1997 JEEP CHEROKEE 2.5L L4
1991-1997 JEEP CHEROKEE 4.0L L6
1991-1992 JEEP COMANCHE 2.5L L4
1991-1992 JEEP COMANCHE 4.0L L6
1991-1997 JEEP WRANGLER 2.5L L6
1991-1997 JEEP WRANGLER 4.0L L6
1993-1997 JEEP GRANDCHEROKEE 4.0L L6
1993-1997 JEEP GRANDCHEROKEE 5.2L V8
1991-1994 DODGE SHADOW 2.2L L4
1991-1994 DODGE SHADOW 2.5L L4
1992 DODGE DAYTONA 2.2L L4
1991-1993 DODGE DAYTONA 2.5L L4
1991-1992 DODGE SPIRIT 2.2L L4
1991-1995 DODGE SPIRIT 2.5L L4
1990-1997 DODGE DAKOTA 2.5L L4
1992-1997 DODGE DAKOTA 3.9L V6
1992-1997 DODGE DAKOTA 5.2L V8
1991-1995 DODGE CARAVAN 2.5L L4
1991-1993 DODGE DYNASTY 2.5L L4
1995 DODGE STRATUS 2.5L V6
1992-1994 DODGE B150 3.9L V6
1992-1994 DODGE B150 5.2L V8
1995-1997 DODGE B1500 3.9L V6
1995-1997 DODGE B1500 5.2L V8
1992-1994 DODGE B250 3.9L V6
1992-1994 DODGE B250 5.2L V8
1992-1994 DODGE B250 5.9L V8
1995-1997 DODGE B2500 3.9L V6
1995-1997 DODGE B2500 5.21 V8
1995-1997 DODGE B2500 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE D150PICKUP 3.9L V6
1992-1993 DODGE D150PICKUP 5.2L V8
1993 DODEE D150PICKUP 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE D250PLCKUP 3.9L V6
1992-1993 DODGE D250PLCKUP 5.2I V8
1992-1993 DODGE D250PLCKUP 5.9L V8
1994-1997 DODGE RAM1500PICKUP 3.9L V6
1994-1997 DODGE RAM1500PICKUP 5.2L V8
1994-1997 DODGE RAM1500PICKUP 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE W150PICKUP 3.9L V6
1992-1993 DODGE W150PICKUP 5.2L V8
1993 DODGE W150PICKUP 5.9L V8
1992-1994 DODGE B350 5.2L V8
1992-1994 DODGE B350 5.9L V8
1995-1997 DODGE B3500 5.2L V8
1995-1997 DODGE B3500 5.9L V8
1994-1996 DODGE RAM2500PICKUP 5.2L V8
1994-1997 DODGE RAM2500PICKUP 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE RAMCHARGER 5.2L V8
1992-1993 DODGE RAMCHARGER 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE W250PICKUP 5.2L V8
1992-1993 DODGE W250PICKUP 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE D350PICKUP 5.9L V8
1994-1997 DODGE RAM3500PICKUP 5.9L V8
1997 DODGE RAM3500WAN 5.9L V8
1995-1996 DODGE RAM400 5.9L V8
1992-1993 DODGE W350PICKUP 5.9L V8
1991-1994 PLYMOUTH SUNDANCE 2.2L L4
1991-1994 PLYMOUTH SUNDANCE 2.5L L4
1991-1995 PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM 2.5L L4
1991-1995 PLYMOUTH VOYAGER 2.5L L4
Basic Function
1. Voltage Transformation: The ignition coil takes the 12-volt (or similar) battery voltage and steps it up to around 20,000 to 50,000 volts.
2. Generation of Spark: This high-voltage output is then sent to the spark plugs via the distributor (in older cars) or directly (in many modern cars with coil-on-plug systems). When the high voltage reaches the spark plug, it jumps the gap between the electrodes, creating a spark that ignites the air-fuel mixture in the engine's cylinder.
Construction
- Primary Coil: The primary coil is typically a few hundred turns of heavy wire, through which the low voltage current flows when the ignition is on.
- Secondary Coil: The secondary coil is made of thousands of turns of much finer wire, which induces the high voltage necessary for spark generation.
Types
- Distributor Ignition System: Older cars often use a single ignition coil that supplies voltage to all spark plugs through a distributor and spark plug wires.
- Coil-on-Plug: Modern engines may use a separate ignition coil for each spark plug, mounted directly on top of the plug, which improves efficiency and reliability.
Importance
- Reliable ignition coils are crucial for engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
- Faulty ignition coils can cause misfires, rough idling, and poor acceleration, leading to decreased performance and potential damage to the engine over time.
Common Issues
- Coil Failure: Over time, coils can wear out or fail due to heat, vibration, or electrical issues.
- Misfires: A malfunctioning ignition coil can cause engine misfires, which may trigger the check engine light and reduce fuel efficiency.
Diagnosis and Replacement
- Diagnosis: Issues with ignition coils can be diagnosed using diagnostic tools that read engine codes and check for misfire counts.
- Replacement: When an ignition coil fails, it's often recommended to replace all coils at once or those in the same coil pack to maintain engine balance and prevent future failures.
Ignition coils are thus essential components that play a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation and performance of internal combustion engines.
Send your message to us: